Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks (12/12/2014)
Famoso paper introduttivo dei modelli sequence-to-sequence per i task di traduzione automatica, uno degli autori è Ilya Sutskever.
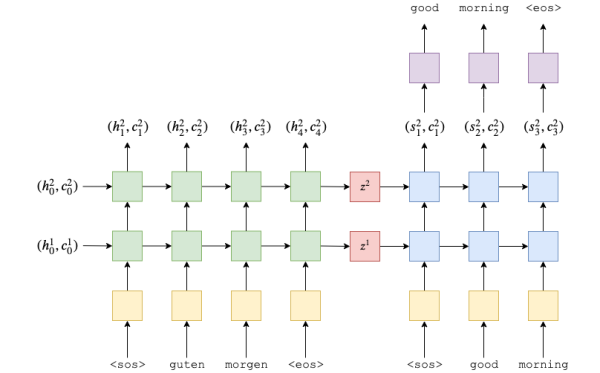
Funzionamento in breve
L'encoder:
- Prende, uno alla volta, un vettore in formato one-hot che rappresenta l'ID nel vocabolario sorgente
- Questo passa in un layer denso nn.Embedding, che aiuterà la rete a "risistemare" gli ID dalla rappresentazione sparsa one-hot a quella densa, semantica, di Embedding
- Passa in (quattro nel paper) layer LSTM, che torna uno stato nascostom che cattura i cambiamenti più recenti, e un "cell state", che cattura le dipendenze a lungo termine
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, n_layers, dropout):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_dim, embedding_dim)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, n_layers, dropout=dropout)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, src):
# src = [src length, batch size]
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(src))
# embedded = [src length, batch size, embedding dim]
outputs, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedded)
# outputs = [src length, batch size, hidden dim * n directions]
# hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# outputs are always from the top hidden layer
return hidden, cell
Il decoder:
- Riceve l'input, che è <start or sentence> oppure l'ultimo token generato
- Riceve hidden e cell state e li inserisce nel (nei) layer LSTM. Alla prima iterazione questi sono quelli del decoder.
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_dim, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, n_layers, dropout):
super().__init__()
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_dim, embedding_dim)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, n_layers, dropout=dropout)
self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, input, hidden, cell):
# input = [batch size]
# hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# n directions in the decoder will both always be 1, therefore:
# hidden = [n layers, batch size, hidden dim]
# context = [n layers, batch size, hidden dim]
input = input.unsqueeze(0)
# input = [1, batch size]
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(input))
# embedded = [1, batch size, embedding dim]
output, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedded, (hidden, cell))
# output = [seq length, batch size, hidden dim * n directions]
# hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# seq length and n directions will always be 1 in this decoder, therefore:
# output = [1, batch size, hidden dim]
# hidden = [n layers, batch size, hidden dim]
# cell = [n layers, batch size, hidden dim]
prediction = self.fc_out(output.squeeze(0))
# prediction = [batch size, output dim]
return prediction, hidden, cell
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, device):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.device = device
assert (
encoder.hidden_dim == decoder.hidden_dim
), "Hidden dimensions of encoder and decoder must be equal!"
assert (
encoder.n_layers == decoder.n_layers
), "Encoder and decoder must have equal number of layers!"
def forward(self, src, trg, teacher_forcing_ratio):
# src = [src length, batch size]
# trg = [trg length, batch size]
# teacher_forcing_ratio is probability to use teacher forcing
# e.g. if teacher_forcing_ratio is 0.75 we use ground-truth inputs 75% of the time
batch_size = trg.shape[1]
trg_length = trg.shape[0]
trg_vocab_size = self.decoder.output_dim
# tensor to store decoder outputs
outputs = torch.zeros(trg_length, batch_size, trg_vocab_size).to(self.device)
# last hidden state of the encoder is used as the initial hidden state of the decoder
hidden, cell = self.encoder(src)
# hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# first input to the decoder is the <sos> tokens
input = trg[0, :]
# input = [batch size]
for t in range(1, trg_length):
# insert input token embedding, previous hidden and previous cell states
# receive output tensor (predictions) and new hidden and cell states
output, hidden, cell = self.decoder(input, hidden, cell)
# output = [batch size, output dim]
# hidden = [n layers, batch size, hidden dim]
# cell = [n layers, batch size, hidden dim]
# place predictions in a tensor holding predictions for each token
outputs[t] = output
# decide if we are going to use teacher forcing or not
teacher_force = random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio
# get the highest predicted token from our predictions
top1 = output.argmax(1)
# if teacher forcing, use actual next token as next input
# if not, use predicted token
input = trg[t] if teacher_force else top1
# input = [batch size]
return outputs
Link
https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.3215
